Dermatitis is more than just an itchy rash—it’s an inflammation of the skin that can affect anyone at any age. While it may appear as a minor irritation initially, persistent dermatitis can take a toll on your skin health, self-esteem, and overall quality of life. Understanding the causes and triggers is essential to prevent flare-ups, manage symptoms, and protect your skin in the long term.
This guide explores the different types of dermatitis, the underlying causes—from allergens to lifestyle factors—and provides practical strategies for prevention and treatment. Whether you’re dealing with occasional flare-ups or chronic irritation, this article offers expert insights to help you regain healthy, comfortable skin.
Understanding Dermatitis
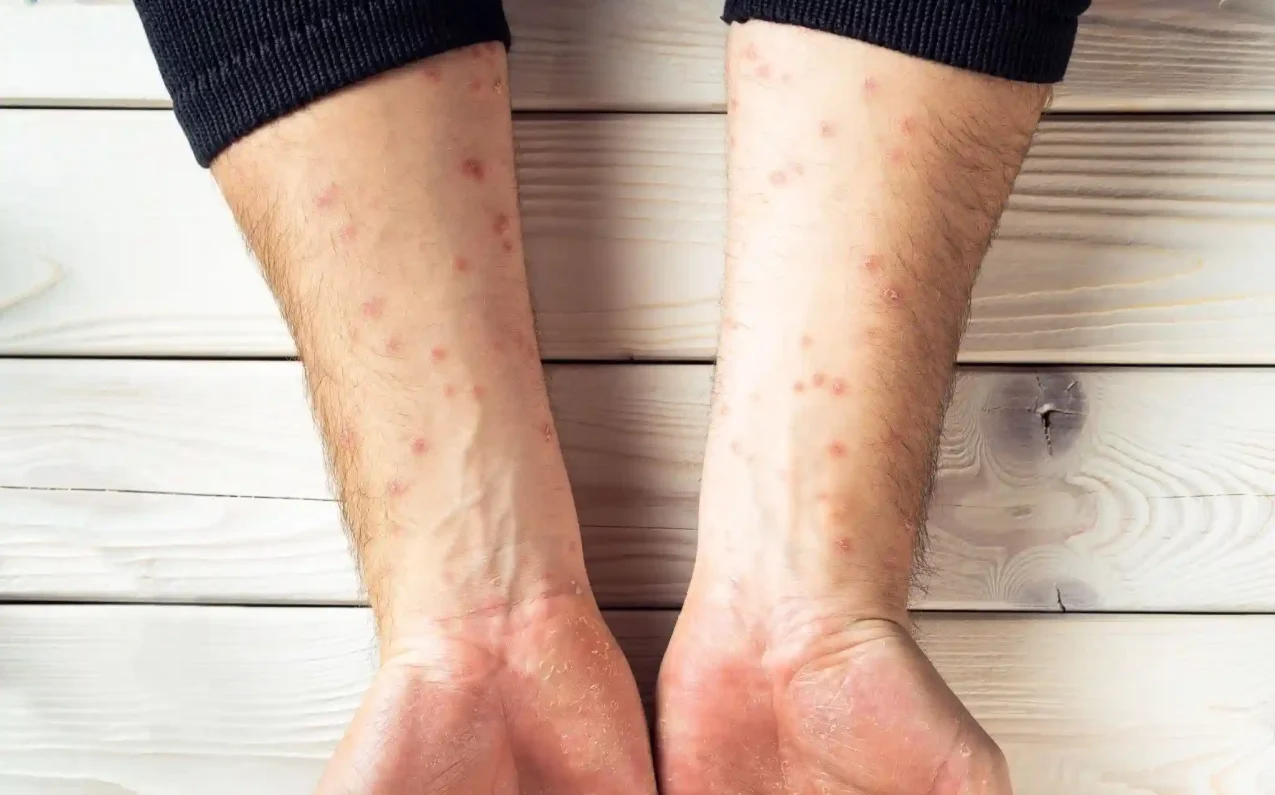
Dermatitis is a broad term for skin inflammation, which can range from mild redness to severe irritation with swelling and blisters. The condition occurs when the skin’s natural barrier is compromised, allowing irritants, allergens, or pathogens to trigger an immune response.
Dermatitis can be acute or chronic. Acute dermatitis appears suddenly, often due to direct exposure to an irritant, and usually resolves within a few days with proper care. Chronic dermatitis persists for months or years, leading to thickened skin, discoloration, and recurring discomfort.
How Skin Responds to Inflammation
- Immune cells and histamine are released in response to irritants or allergens.
- Common signs include redness, swelling, itching, and sometimes blister formation.
- Scratching can worsen inflammation and lead to secondary infections.
- Untreated dermatitis can compromise the skin barrier, making flare-ups more frequent.
Allergic Causes of Dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis occurs when the immune system overreacts to harmless substances. Common allergens include pollen, dust mites, animal dander, and certain cosmetic ingredients. These triggers can cause a hypersensitive reaction, leading to redness, swelling, and intense itching.
Contact Dermatitis from Allergens
A specific type of allergic dermatitis, contact dermatitis, develops when skin comes into direct contact with irritants or allergens. Metals like nickel, fragrances in skincare products, and harsh detergents are frequent culprits. Identifying triggers is key—patch testing or keeping a diary of exposure can help pinpoint the cause. Once identified, avoiding contact with these substances is the most effective prevention strategy.
Irritant Causes of Dermatitis
Unlike allergic reactions, irritant dermatitis results from direct damage to the skin rather than an immune response. It can be caused by chemicals, mechanical friction, or environmental factors such as extreme temperatures or pollutants. Frequent hand washing, exposure to cleaning products, or occupational contact with harsh substances increases the risk.
Lifestyle and occupational habits play a significant role. For example, healthcare workers, hairdressers, and factory workers often experience repeated skin irritation, which can become chronic if protective measures aren’t taken.
Infections Leading to Dermatitis
Sometimes, dermatitis is a result of infections, either bacterial, fungal, or viral. Scratching inflamed skin can break the barrier, allowing pathogens to enter and worsen the condition. Early recognition is crucial to prevent chronic skin problems.
Fungal and Bacterial Dermatitis
Common bacterial causes include Staphylococcus aureus, while fungal infections may involve Candida species. Symptoms can include pustules, scaling, redness, and localized warmth. Maintaining hygiene, avoiding scratching, and using targeted antimicrobial treatments are vital to control these infections and prevent recurrence.
Genetic and Autoimmune Factors
Genetics can significantly influence dermatitis susceptibility. Atopic dermatitis and psoriasis are examples where hereditary factors increase the risk. Autoimmune-related skin issues occur when the body’s immune system attacks healthy skin cells, causing chronic inflammation.
Environmental triggers often interact with genetic predispositions, meaning even someone genetically prone to dermatitis may experience fewer flare-ups by managing external triggers effectively.
Lifestyle and Environmental Triggers
Everyday habits and environmental factors can aggravate dermatitis. Diets high in processed foods or sugar, chronic stress, and inconsistent hygiene routines may worsen inflammation. Similarly, weather extremes, humidity, and pollution can trigger flare-ups or prolong healing.
Practical lifestyle adjustments—like stress management, balanced nutrition, and avoiding harsh environmental exposures—play a crucial role in maintaining healthy skin.
Symptoms and Early Warning Signs
Recognizing dermatitis early allows for timely intervention. Common symptoms include:
- Itching, redness, or a burning sensation
- Scaling, flaking, or dry patches
- Swelling or mild blistering
Chronic dermatitis may lead to thickened skin, discoloration, or hyperpigmentation. Monitoring your skin for these signs and seeking medical advice promptly can prevent long-term complications.
Prevention Strategies for Dermatitis
Preventing dermatitis revolves around reducing exposure to known triggers and maintaining skin integrity. Key strategies include:
- Avoiding allergens and irritants in cosmetics, detergents, or metals
- Using gentle skincare routines, including moisturizers and mild cleansers
- Wearing protective clothing during exposure to harsh chemicals or extreme weather
Daily Skin Care Tips
- Hydrate skin consistently with barrier-repair creams.
- Avoid harsh soaps, scrubs, or exfoliants that strip natural oils.
- Monitor changes in your skin regularly.
- Maintain a healthy skin microbiome using mild, balanced products.
Preventive care is always more effective than treating flare-ups after they occur.
Treatment Approaches for Dermatitis
Managing dermatitis often requires a combination of topical treatments, systemic therapy, and lifestyle modifications.
- Topical treatments: Corticosteroids, anti-inflammatories, and barrier creams reduce inflammation and restore skin function.
- Systemic therapy: In severe cases, oral medications may be prescribed to control widespread or persistent dermatitis.
- Lifestyle-based strategies: Stress management, dietary changes, and proper skin hygiene complement medical interventions.
Medical Interventions and Therapy Options
When over-the-counter products fail, dermatologists may recommend:
- Prescription-strength topical corticosteroids or immunomodulators
- Phototherapy for chronic or resistant cases
- Emerging treatments like biologics for autoimmune-related dermatitis
Combining professional care with preventive measures ensures the best long-term outcomes.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek medical attention if you experience:
- Severe or widespread dermatitis
- Persistent itching or pain unrelieved by home care
- Signs of infection, such as pus, fever, or spreading redness
Self-treating without proper diagnosis can worsen the condition or mask underlying causes. A dermatologist can provide a personalized plan, balancing treatment with preventive strategies.
Conclusion
Dermatitis can be challenging, but understanding its causes empowers you to manage it proactively. Identifying triggers, maintaining a consistent skincare routine, and seeking professional guidance are critical to reducing flare-ups and protecting skin health. By taking a holistic approach—combining prevention, monitoring, and expert care—you can maintain healthy, comfortable skin and improve your quality of life.
FAQs About Dermatitis
1. What triggers dermatitis most commonly?
Dermatitis can be triggered by allergens, irritants, infections, genetic factors, stress, or environmental conditions like extreme weather or pollution.
2. How can I prevent dermatitis flare-ups at home?
Regular moisturizing, avoiding known irritants, using gentle skincare, and protective clothing are essential steps to prevent flare-ups.
3. Can diet influence dermatitis?
Yes. Diets high in processed foods, sugar, or allergens can worsen inflammation, while balanced nutrition may support skin health.
4. When should I see a dermatologist for dermatitis?
Seek professional care if symptoms are severe, persistent, spreading, or showing signs of infection. Early intervention prevents complications.
5. Are natural remedies effective for dermatitis?
Some natural remedies, like oatmeal baths or aloe vera, can soothe mild symptoms, but they should complement, not replace, medical treatment.